An insulin pump is a small electronic device, about 5.3cm wide and 9.6cm tall. The pump can help you mimic the way a healthy pancreas functions, replacing the need for frequent injections. The pump delivers precise doses of rapid-acting insulin 24 hours a day, to match your body’s needs.
*For assistance in India, please contact the India Helpline: 1800-209-6777
ALL 365 DAYS of the Year with extended working window of 12 hours.
New Timing : 9:30am to 9:30pm
All 7 days of the week
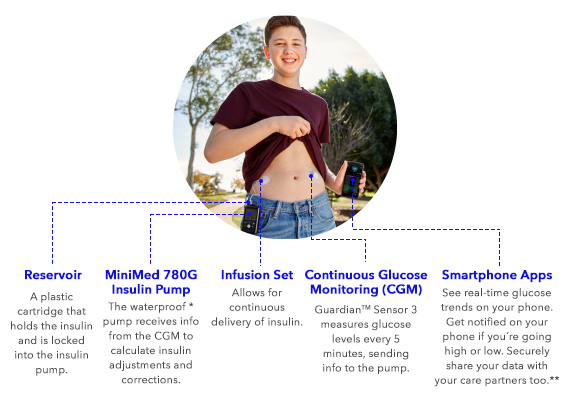
COMPONENTS OF INSULIN PUMP THERAPY
A small, durable electronic device to program your insulin and show you how you are tracking. The device includes a reservoir compartment.
LEARN MOREAn infusion set includes a thin cannula that goes from the reservoir to the infusion site on your body. The cannula is inserted into the site -similar to where you would give insulin injections. The infusion set is changed every two to three days.
LEARN MOREA plastic cartridge that holds the insulin and is locked into the insulin pump. A reservoir can hold up to 300 units of insulin and is changed every two to three days.
GuardianTM Sensor 3 measures glucose levels every 5 minutes, sending info to the pump.
LEARN MORESee real-time glucose trends on your phone. Get notified on your phone if you’re going high or low. Securely share your data with your care partners too.

- Blood Glucose Meter: Wirelessly transmits your BG readings to your pump.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A transmitter and sensor wirelessly transmit your glucose readings to your pump, giving you early warnings of highs and lows, lowering HbA1c levels9 & reducing the time of hypos10.
- Carelink® Software: An online tool allowing you to track your insulin usage and its levels during your daily activities.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF INSULIN PUMP THERAPY?
Insulin pump therapy offers multiple clinical benefits over multiple daily injection therapy.1,2
Get better
glucose control3
With our pump and sensor system, you’re four times more likely to reach your target A1C4. You can also reduce low glucose episodes by up to 84 percent and lower the risk of long-term complications.5,6
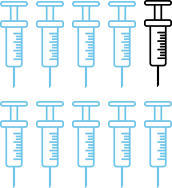
90%fewerinjections8

Kidney Damage reduced up to6
54%
Cardiovascular Damage reduced up to6
41%
Nerve Damage reduced up to6
41%
eye Damage reduced up to6
53%Better HbA1c1,2 Control
Fewer hypoglycaemic events2
Easier dosing, accurate dosing,no needles
Greater flexibilityin when to eat and how to exercise
IS INSULIN PUMP THERAPY RIGHT FOR ME?
Many people with Insulin Dependent diabetes may benefit from an insulin pump, but aren't aware of the benefits. In general you could get better control with an insulin pump if you experience any of the following:
You may be interested in
- J. C. Pickup and A. J. Sutton Severe hypoglycaemia and glycemic control in Insulin Dependant Diabetes: meta-analysis of multiple daily insulin injections compared with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion Diabetic Medicine 2008 :25, 765–774.
- Bergenstal RM1, Tamborlane WV, Ahmann A, Buse JB, Dailey G, Davis SN, Joyce C, Perkins BA, Welsh JB, Willi SM, Wood MA; STAR 3 Study Group. Sensor-augmented pump therapy for A1C reduction (STAR 3) study: results from the 6-month continuation phase. Diabetes Care. 2011 Nov;34(11):2403-5. doi: 10.2337/dc11-1248. Epub 2011 Sep 20.
- Battelino T, Conget I, Olsen B, et al. The use and efficacy of continuous glucose monitoring in Type 1 diabetes treated with insulin pump therapy: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetologia. 2012;55:3155–3162.
- Doyle EA, Weinzimer SA, Steffen AT, Ahern JAH, Vincent M, Tamborlane WV. A randomized prospective trial comparing the efficacy of insulin pump therapy with multiple daily injections using insulin glargine. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(7):1554–1558.
- Bode BW, Steed RD, Davidson PC. Reduction in severe hypoglycemia with long-term continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in Type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1996;19:324–327.
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–986.
- Excluding Sure-T
- Assumes four injections per day for 30 days and one infusion set change every three days.
- Kaufman FR, et al. A pilot study of continuous glucose monitoring system. Diab Care. 2001:24:2030-2034
- User Evaluations. Data on File, Medtronic MiniMed, Inc., Northridge, CA.